Congratulations to the 2022 Biology Instructional Office Outstanding Teaching Award Recipients:Laura GonzalezJonathan Partridge |
Awards & Honors Throughout the Years
SUZANNE BARTH |
2017- Biology Instructional Office Teaching Excellence Award 2006- College of Natural Sciences Teaching Excellence Award |
MARK BIERNER |
2005-Natural Sciences Council Faculty Services Award |
ELIZABETH (JANE) BRADBURY |
2021- COVID Transformational Online Instruction Contributions (TONIC) Award |
KATHERINE BRUNER |
2021- COVID Transformational Online Instruction Contributions (TONIC) Award 2021- Biology Instructional Office Teaching Excellence Award 2020- College of Natural Sciences Teaching Excellence Award 2020- Center for Skills & Experience Flags Online Course Conversion Award |
RUTH BUSKIRK |
2013- Texas Exes Texas 10 Award 2013- President's Associates Teaching Excellence Award 2012- The Plan II Honors Program Chad Oliver Teaching Award 2009- Regents Outstanding Teaching Award, The University of Texas System 2009- National Academies Education Fellow in the Life Sciences 2008- National Academies Education Fellow in the Life Sciences 2003- College of Natural Sciences Teaching Excellence Award 2003- Alpha Lambda Delta and Phi Eta Sigma Teaching Excellence Award 2000- Alpha Lambda Delta and Phi Eta Sigma Teaching Excellence Award 1998- Alpha Lambda Delta and Phi Eta Sigma Teaching Excellence Award 1998- Texas Exes Excellence Teaching Award 1996- Natural Science Advisory Council Teaching Excellence Award 1995- Parents' Association, Centennial Teaching Fellowship 1994- Alpha Lambda Delta and Phi Eta Sigma Teaching Excellence Award 1994- Natural Science Advisory Council Teaching Excellence Award 1993- Natural Science Advisory Council Teaching Excellence Award 1991- Texas Exes Excellence Teaching Award 1988- Texas Exes Excellence Teaching Award |
ERIC CAMBRONNE |
2021- Biology Instructional Office Teaching Excellence Award |
PETER ENGLISH |
2009- Natural Sciences Council Faculty Service Award 2021- Biology Instructional Office Teaching Excellence Award |
Jennifer fritz |
2020- Office of the Executive Vice President and Provost Experiential Learning Initiative Award (Course Developer Program) 2019- Cale McDowell Award for Teaching Excellence 2019- Biology Instructional Office Teaching Excellence Award 2011- Faculty Award from the Services for Students with Disabilities |
LAURA GONZALEZ |
2022- Biology Instructional Office Teaching Excellence Award 2020- Natural Sciences Council Faculty Service Award 2020- Office of the Executive Vice President and Provost Experiential Learning Initiative Award (Course Developer Program) |
CYNTHIA LABRAKE |
2021- COVID Transformational Online Instruction Contributions (TONIC) Award 2017- University of Texas Senior Provost Teaching Fellow and Chair of Program (elected by peers) 2015- University of Texas Provost Teaching Fellow 2014- University of Texas President’s Associates Teaching Excellence Award 2010- University of Texas Regent’s Outstanding Teaching Award 2009- University of Texas Dad’s Club Centennial Teaching Fellow 2003-University of Texas Natural Sciences Teaching Excellence Award |
TRAVIS LADUC |
2019- College of Natural Sciences Teaching Excellence Award |
ANITA LATHAM |
2019- Services for Students with Disabilities Appreciation Awards 2016- President’s Associates Teaching Excellence Award 2016-Services for Students with Disabilities Appreciation Awards 2015- Regents’ Outstanding Teaching Award 2015- Services for Students with Disabilities Appreciation Awards 2009- The College of Natural Sciences Teaching Excellence Award 2009- Natural Sciences Council Faculty Service Award 2009- Texas Blazers Faculty Excellence Award |
MARTY MAAS |
2021- Biology Instructional Office Teaching Excellence Award |
JAN MACHART |
2019- Biology Instructional Office Teaching Excellence Award |
BLINDA MCCLELLAND |
2021- Helping Hands Tower Award 2015- Biology Instructional Office Teaching Excellence Award |
GENE MCDONALD |
2016-Biology Instructional Office Teaching Excellence Award |
Kay Mcmurry |
2017- Biology Instructional Office Teaching Excellence Award |
JENNIFER MOON |
2020- Member of Distinguished Service Academy 2019- Natural Science Council Faculty Service Award 2017- President's Associates Teaching Excellence Award 2016- Provost's Teaching Fellow 2015-Regents’ Outstanding Teaching Award 2012- Natural Science Council Faculty Service Award in the College of Natural Sciences 2011- College of Natural Sciences Teaching Excellence Award in SBS 2011- College of Natural Sciences Science Outreach Award Honorable Mention |
Jonathan PaRTRIDGE |
2023- Certificate of Recognition, Disability and Access UT Austin 2022- Biology Instructional Office Teaching Excellence Award 2022- Students as Partners Award, Center for Teaching and Learning |
KRISTIN PATTERSON |
2021- COVID Transformational Online Instruction Contributions (TONIC) Award 2020- Provost’s Teaching Fellows Innovation Award 2018- Provost's Teaching Fellow 2018- College of Natural Sciences Teaching Excellence Award 2016- Biology Instructional Office Teaching Excellence Award 2015- National Academies Teaching Fellow |
STACIA RODENBUSCH |
2012- College of Natural Sciences Teaching Excellence Award |
K. SATA SATHASIVAN |
2021- COVID Transformational Online Instruction Contributions (TONIC) Award 2013- Board of Regents Outstanding Teaching Award 2011- Natural Sciences Council Faculty Service Award 2009- Gold Award for the best instructional innovation at UT Austin for Quest 2007- Division for Instructional Innovation and Assessment Faculty Service Award 2006 -Texas Exes Teaching Award 2005- Dad’s Centennial Teaching Fellowship Award, 2005. The University of Texas Austin 1999- School of Biological Sciences Teaching Excellence Award |
ANN THIJS |
2021- COVID Transformational Online Instruction Contributions (TONIC) Award 2021- College of Natural Sciences Teaching Excellence Award |
EMIN ULUG |
2007- College of Natural Sciences Teaching Excellence Award 2021- Biology Instructional Office Teaching Excellence Award |




Congratulations to Our 2022 Teaching Assistant Award Winners!
On Tuesday, May 10th, 2022 the Biology Instructional Office announced the winners of the 21-22 BIO Oustanding Teaching Assistant award. Out of over 200 TA positions appointed during the past year, we had 9 TAs and 10 UGTAs nominated for this honor, but could choose only 6 to win the award. The list below includes all of the nominees. Winners are indicated by *.
We would like to thank these TAs & UGTAs, both the award winners and those nominated, for being outstanding teaching assistants. TAs are an integral part of the teaching experience and you have gone above and beyond what has been asked of you. Thank you!
2022 TA Award Nominees |
||
| Winners indicated by * | ||
TA Name |
Nominator |
Course |
| Caitlyn Wilson* | Katie Bruner | BIO 325L |
| Emily Lessig* | Hans Hoffman | BIO 361T |
| Esteban Cantu | Anita Latham | BIO 311C |
| Haley Hardtke | Jessie Zhang | BCH 370 |
| Nicole Butler | Marty Maas | BIO 206L |
| Nicole Johnson | Susanne Ressl | NEU 337 |
| Soroosh Sadeh | David Cannatella, William Babler | BIO 446L |
| Sten Stray-Gundersen* | Jan Machart | BIO 165U |
| Viviana June | Inder Saxena | BIO 325 |
UGTA NAME |
Nominator |
Course |
| Catherine Tang | Inder Saxena | BIO 325 |
| Jackson Burns* | Ann Thijs | BIO 311D |
| Joanna Lee | Ian Cheng | BIO 365S |
| Lais Haddad | Marty Maas | BIO 206L |
| Paul Fliedner* | Shelley Payne | BIO 361 |
| Roman Martinez | Goheun Kim | BIO 325 |
| Shalini Ramachandran* | Jennifer Fritz | BIO 311C |
| Sierra Wood | Pratibha Saxena | BIO 326M |
| Simran Shah | Pratibha Saxena | BIO 326M |
| Tammy Huynh | Jonathan Partridge | BIO 311C |
See our past TA Award Nominees & Winners
New Employees
Biology Instructional Office Administrative Contact Information |
||
|
Janice Fischer Director of Biology Instructional Office (512) 232-3690 janicefischer@austin.utexas.edu NMS 2.312 |
Greg Browning Administrative Manager (512) 232-7073 MBB 1.220G |
Laura Evans Financial Manager (512) 471-1147 MBB 1.230
|
|
Belen Byers Senior Administrative Associate (512) 232-2713 MBB 1.220K |
Aletha Irby Senior Administrative Associate (512) 232-7963 MBB 1.220HB |
Angela Kizzee Senior Procurement Officer (512) 232-6438 MBB 1.206 |
UT Austin New Employee Checklist
1. New Employee Welcome and Orientation — If you're benefits eligible, we strongly recommend that you attend New Employee Welcome and Orientation on your first day of employment in order to complete many items on this checklist. You may register yourself for this course, which is available in UTLearn (EID required).
To register:
-
- Use the search feature in the upper right corner.
-
-
Type in "New employee"
-
Select "PN 1000 - New Employee Welcome and Orientation"
-
Select the session you'd like to attend and click "Request"
-
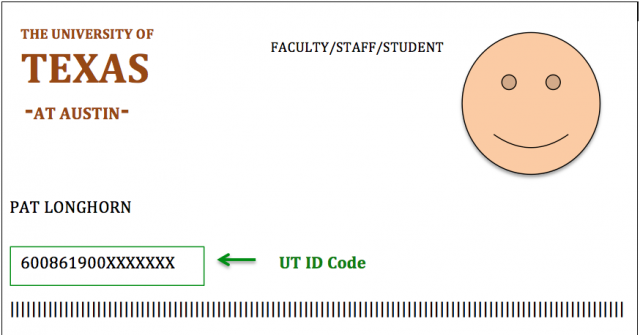
2. ID Card and EID — You can get your ID card at orientation or at the ID Center, located on the first floor of the FAC. Bring proof of identity (government issued ID with your picture), to get your ID card and upgrade your UT Electronic Identification (EID). This step is very important. You'll need to upgrade your EID before you can access most online services for employees.
3. Payroll Information — Complete My Paycheck Profile online. You will need an upgraded EID and information from your UT ID card to complete this online form.
4. Employment Eligibility Verification (I-9) — You must complete this electronic form no later than your first work day. You will be required to present original documents from the List of Acceptable Documents to prove your identity and authorization to work in the United States. Information from your documents will be submitted to the federal E-Verify system for verification. Please contact your hiring department if you have not been told where to bring your documents. If you receive an email with the subject line, Electronic I-9 Shuttle Request, please follow the instructions to complete the employee section of the form.
5. Criminal Background Check Request – You should have received an email requesting electronic authorization to conduct a background check. If you have not received the email or completed the background check request, please contact your hiring department.
6. Acknowledge the Ethics Statement* — Read and acknowledge the Standards of Conduct and Political Activities online (EID required).
7. UT System Worker’s Compensation Insurance Health Care Network Notification – Read and acknowledge theWorker’s Compensation Network Acknowledgement Form online (EID required).
8. Health Insurance Marketplace Notice – The Affordable Care Act (ACA) requires employers to provide this notice to all employees about the option to shop in the Marketplace (also known as the “exchange”). More information about ACA and UT Select is available on the OEB website.
9. Selective Service Eligibility — If you're a male between the ages of 18 and 25, complete the Selective Service Eligibility and Verification online. For more information, see the Selective Service Registration Frequently Asked Questions page.
10. Conflicts of Interest Policy — Read both the policy and the statute of law concerning conflicts of interest within three business days. For additional information please visit the Provost Office's Conflict of Interest webpage.
11. Outside Employment — If you are working for another employer, you must complete an outside employment form and gain proper approval. If you are an exempt employee, prior approvals need to be completed through the portal: Outside Activity Portal 5-2011 If you are unsure about your status under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) check one of your individual time reports on the electronic timesheet system and look at your FLSA status.
12. Employee Information* — Complete your employee biographical information and your veteran status information online.
Your First Week
1. Insurance Coverage — Review the New Employee Benefits Enrollment Checklist for details about how to complete your enrollment. You must make your insurance elections online during your Initial Benefits Enrollment period, which is the first 31 calendar days of employment. If you do not make elections and you are a full-time employee, you will default to the Basic Coverage only. If you are a part-time employee, you will forfeit insurance coverage altogether if elections are not made.
2. Compliance Training — Begin your compliance training. This training must be completed within your first 30 days of employment. For alternate methods of taking the training, call the compliance training coordinator at 512-232-7842.
3. Read and acknowledge the Compliance and Ethics Guide [PDF]. After reviewing all sections of the Guide, advance to the Acknowledgment Page where you will record your agreement to act in accordance with UT Austin’s requirements for ethical conduct.
4. Acceptable Use Policy — Acknowledge the Information Resources Acceptable Use and Security Policy Agreement.
5. Supervisor Meeting — Talk with your supervisor about your job description, performance expectations, probationary period, and performance evaluation.
6. Keys — Pick up your key(s) at the Locks and Keys office located in the Service Building. Remember to take the key request form given to you by your department and your ID card.
7. Parking Permit — Visit the Parking and Transportation website for information about parking on campus. If you don't plan to commute by car, check out alternative transportation options.
8. Prior State Service — If you have worked for any other State of Texas agency or public university, print a Transfer of State Service [PDF] form and and fax it to Human Resources. Read more about prior state service transfer.
9. Timesheets — Complete your timesheets online in the Time Report System. Talk to your supervisor, if you are unable to access your timesheet.
10. Nonresident Aliens — Please be sure you have completed your GLACIER record. You should receive your login instructions via the UT Secure Message System within two weeks of beginning employment. Send the forms generated from GLACIER and required immigration documents to Payroll Services.
YOUR FIRST MONTH
1. Insurance Coverage — Make sure you’ve reviewed the New Employee Benefits Enrollment Checklist and made your elections online within the first 31 calendar days of your employment.
2. Compliance Training — Make sure you've completed your compliance training.
Purchasing and Reimbursement
There are 4 options for ordering class & office materials:
- Submit a Purchase Order to Angela Kizzee via Request System and assign to kizzeeaj. Instuctions to complete Request order can be found here.
- Create a shopping cart and assign it to Angela Kizzee via UT Market
- Purchase online or in person with your official procurement card Purchase online or in person with your personal credit card for entertainment purchases and submit the following to Angela Kizzee for reimbursement within 30 days:
- completed Official Occasion Expense Form
- itemized receipt
NOTE: Per UT Purchasing Policy, all departmental purchases should be processed by our purchaser, Angela Kizzee. If a purchase cannot be done thought Request System, UTMarket or Angela's procard, please contact her prior to purchasing. Purchases for the university made by faculty, staff, and students using personal funds are not authorized and will only be reimbursed as an exception.
Maintenance and Service Requests
- Facility Services Work Order Request and Query
- Please fill out the work order request and send a screenshot to laura.evans@utexas.edu for submission
- Room Reservations
Keys, Keycard Access, and Locknetics
Requests for access to buildings using the Proximity Access system should be sent to the appropriate building manager:
PROXIMITY ACCESS TO BUILDINGS |
||
| BUILDING | MANAGER | CONTACT INFORMATION |
| BME Proximity Access | Bobby Knight |
Office: BME 3.314A Email: bmknight@mail.utexas.edu Phone: (512) 921-0334, (512) 471-7908 |
| MBB Building Proximity Access | Dwaine Benson |
Office: MBB 2.404 Email:dwaine.benson@austin.utexas.edu Phone: (512) 232-2178, URGENT: (979) 218-1012 |
| NHB Building Proximity Access |
Cory Konieczny |
Office: NHB 1.404 Email: cory.konieczny@austin.utexas.edu Phone: (512) 769-0448 |
| NMS Building Proximity Access | Dwaine Benson |
Office: MBB 2.404 Email: dwaine.benson@austin.utexas.edu Phone: (512) 232-2178, URGENT: (979) 218-1012 |
Physical Key Requests: Fill out the Physical Key Request Form and email it laura.evans@utexas.edu for an authorized signature. Once approved, bring the signed form to Locks and Keys located at 304 E. 24th St.
Locknetics: Fill out the Locknetics Request Form and email it laura.evans@utexas.edu. Please allow up to 5 business days for programming. You will receive a confirmation email when programming has been completed.
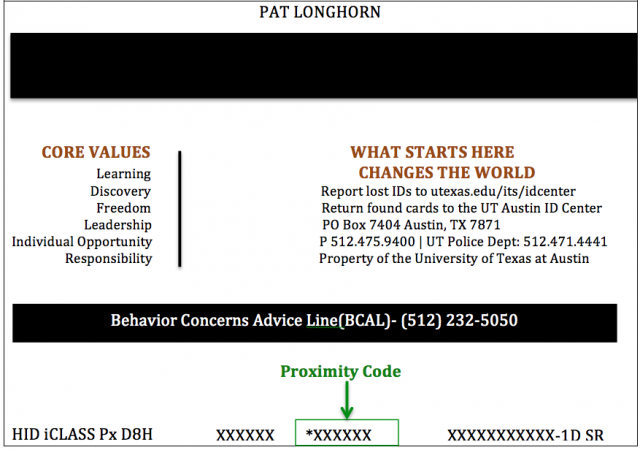
*Note: If your lockentics use proximity, please submit the proximity code on the back of your UT ID.
|
FRONT OF ID CARD |
BACK OF ID CARD |
|
|
Process of Science: Engage in the process of science by practicing observation, generating hypotheses, designing testable experiments and manipulating data. |
|
Quantitative Reasoning: Manipulate numerical data and evaluate the significance of the data using appropriate mathematical and/or statistical methods. |
|
Critical Thinking: Use logical reasoning to apply known concepts to novel situations and to identify and evaluate source materials and scholarly literature. |
|
Independent Learning: Demonstrate personal responsibility to set goals and regularly engage in self-assessment of progress towards academic accomplishment. |
|
Exchange of Ideas: Collaborate, discuss, and exchange ideas in a team setting in order to explore creative solutions to complex problems. |
|
Biology and Society: Apply biological concepts to daily life and issues in society. |
LEADERSHIP BY DEPARTMENT
| Dr. Janice Fischer, Director | Biology Instructional Office |
| Dr. Claus Wilke, Department Chair | Integrative Biology |
| Dr. Tim Keitt, Associate Chair of Undergraduate Education | Integrative Biology |
| Dr. Jeff Gross, Department Chair | Molecular Biosciences |
| Dr. Scott Stevens, Associate Chair of Undergraduate Education | Molecular Biosciences |
| Dr. Robert Messing, Department Chair | Neuroscience |
| Dr. John Mihic, Associate Chair of Undergraduate Education | Neuroscience |
| Chair Information Pending | Marine Science |
| Associate Chair of Undergraduate Education Pending | Marine Science |
COURSES BY DEPARTMENT
Biology Instructional Office Courses
Majors Introductory Courses
BIO 311C: INTRODUCTORY BIOLOGY I
Introduction to biological energy transformation, cell structure and physiology, and gene expression. Three lecture hours and one discussion hour a week for one semester.
- Only one of the following may be counted: Biology 301L, 211, 311C. Biology 311C and 212 may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Credit or registration for Chemistry 301 or 301H.
BIO 311D: INTRODUCTORY BIOLOGY II
Introduction to mechanisms of inheritance, evolution, physiology, and species interactions. Three lecture hours and one discussion hour a week for one semester.
- Biology 301L and 311D may not both be counted. Biology 301M and 311D may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Biology 311C with a grade of at least C-.
BIO 206L: INTRODUCTORY LABORATORY EXPERIMENTS IN BIOLOGY
The organizing principles of biology (such as molecular and cellular functions, reproduction, development, homeostatic mechanisms, and organismal physiology and behavior) are used within a comparative and evolutionary framework to train students in modern laboratory techniques, bioinformatics, experimental design, and interpretation of results. One lecture hour and four laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Credit or registration for Biology 311C or 311D.
Basic principles of Mendelism, molecular genetics, structure and function of genes and chromosomes, populations and evolution. Three lecture hours and one discussion hour a week for one semester.
- Biology 325 and 325H may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Biology 311C and 311D with a grade of at least C- in each.
BIO 325L: LAB EXPERIENCE IN GENETICS
Experimentation and direct observation in fundamental aspects of transmission genetics. One lecture hour and four laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: The following with a grade of at least C-: Biology 325 or 325H, and Biology 206L, 208L, 226L, or Environmental Sciences 311.
BIO 315H: ADVANCED INTRO TO GENETICS: HONORS
Basic principles of genetics and cell biology. Emphasis on gene structure and regulation; transmission of heritable traits; structure and function of cells; bacterial and viral genetics; and recombinant DNA technology. Three lecture hours and one discussion hour a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: A score of 5 on the College Board Advanced Placement Examination in Biology and credit or registration for Chemistry 301 or 301H.
BIO 325H: GENETICS: HONORS
Basic principles of genetics and evolution. Emphasis on population genetics and natural selection; structure and function of organ systems; behavioral ecology; and mutational analysis of organismal development. Three lecture hours and one discussion hour a week for one semester.
- Biology 325 and 325H may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Biology 315H with a grade of at least C-.
BIO 372C: BIOLOGY PEER MENTORS IN RESEARCH/TRAINING
Students work as peer mentors and assistants in the teaching of biology, with emphasis on developing instructional materials that teach fundamental biology with real world data. Students mentor students for at least three hours a week in addition to other weekly meetings.
- Prerequisite: Biology 311C, 311D, and Biology 325, or Biology 315H and 325H with a grade of at least B in each; and consent of the undergraduate adviser.
Non-Majors Courses
BIO 302D: SCIENCE LITERACY AND NUMERACY: ECOLOGY & EVOLUTION
Science literacy and numeracy skills are paramount: Methods of inquiry that lead to scientific
knowledge; dealing with quantitative data; correcting common misconceptions regarding
rational and quantitative thought. These skills will be learned in the context of news events that
include all or some of the following topics: Mendelian genetics; microevolution;
macroevolution; population ecology ; community ecology; ecosystem ecology.
BIO 301E: SCIENCE LITERACY AND NUMERACY: GENETICS & GENOMICS
Science literacy and numeracy skills are paramount: Methods of inquiry that lead to scientific
knowledge; dealing with quantitative data; correcting common misconceptions regarding
rational and quantitative thought. These skills will be learned in the context of news events that
include all or some of the following topics: Human genetics; analysis and manipulation of DNA;
genetic testing; assisted reproductive technology; human ancestry; personalized medicine;
forensic genetics.
BIO 302F: SCIENCE LITERACY AND NUMERACY: HUMAN HEALTH & DISEASE
Science literacy and numeracy skills are paramount: Methods of inquiry that lead to scientific
knowledge; dealing with quantitative data; correcting common misconceptions regarding
rational and quantitative thought. These skills will be learned in the context of news events that
include all or some of the following topics: Metabolic diseases, infectious diseases, genetic
diseases – causes, prevention, and treatments.
BIO 302G: SCIENCE LITERACY AND NUMERACY: BIOTECHNOLOGY & THE FUTURE
Science literacy and numeracy skills are paramount: Methods of inquiry that lead to scientific
knowledge; dealing with quantitative data; correcting common misconceptions regarding
rational and quantitative thought. These skills will be learned in the context of news events that
include all or some of the following topics: Climate change; genetically modified organisms;
biomedical technology.
Integrative Biology Courses
Lower Division Courses
BIO 208L: FIELD BIOLOGY
Field projects, laboratory exercises, field trips, and computer simulation exercises to acquaint students with the principles and applications of ecology and some of the experimental and descriptive methods of ecological investigations. One lecture hour and four laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Credit or registration for Biology 311D.
Upper Division Courses
BIO 137: CONFERENCE COURSE-HUMAN BIOLOGY
One lecture hour a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Biology 346 with a grade of at least C-.
BIO 322: STRUCTURE, PHYSIOLOGY, AND REPRODUCTION OF SEED PLANTS
The principles of structure and functioning of higher plants; special attention to the dynamics of growth and development and reproduction. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Biology 325 or 325H with a grade of at least C-, Chemistry 302 or 302H, and concurrent enrollment in Biology 122L.
BIO 122L: STRUCTURE, PHYSIOLOGY, AND REPRODUCTION OF SEED PLANTS LABORATORY
Observation of structure and reproduction in seed plants and employment of experimental techniques that demonstrate physiological processes, especially processes of growth and development. Two laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Concurrent enrollment in Biology 322; and the following with a grade of at least C-: Biology 206L, 208L, 226L or Environmental Sciences 311.
BIO 321G: PRINCIPLES OF COMPUTATIONAL BIOLOGY
Introduces computational methods used in molecular, cellular, organismal, and population biology. Subjects include molecular bioinformatics, modeling and simulation, and network analysis. Three lecture hours and two computer laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: The following with a grade of at least C-: Biology 325 or 325H; Statistics and Data Sciences 328M (or Statistics and Scientific Computation 328M); and Mathematics 408C, 408S, or 408R.
BIO 337J: COMPUTATIONAL BIOLOGY LABORATORY
Overview of computational biology, with emphasis on nucleic acid sequence analysis and databases. Class projects and self-learning exercises. Two lecture hours and three computer laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Biology 325 or 325H, and Statistics and Data Sciences 328M (or Statistics and Scientific Computation 328M) with a grade of at least C- in each.
BIO 340L: BIOLOGY OF BIRDS
Anatomy, physiology, classification, and ecology of birds. Two lecture hours and three laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: The following with a grade of at least C-: Biology 325 or 325H, and Biology 206L, 208L, 226L, or Environmental Sciences 311.
BIO 346: HUMAN BIOLOGY
Introduction to human evolution, genetics, sexuality, senescence, and population growth. Three lecture hours and one discussion hour a week for one semester. Only one of the following may be counted: Biology 301G, 309F, 346. Prerequisite: Biology 325 or 325H with a grade of at least C-.
BIO 351: ECONOMIC BOTANY
An in-depth analysis of the origin of domesticated plant species, the role in nature of plant products, and the ways natural products have been altered through artificial selection. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Biology 325 or 325H with a grade of at least C-.
BIO 359K: PRINCIPLES OF ANIMAL BEHAVIOR
An introduction to the study of animal behavior: descriptive analysis of behavior; physiological basis of behavior; development of behavior; adaptive significance and evolution of behavior; communication and social behavior. Three lecture hours and one discussion hour a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Biology 325 or 325H with a grade of at least C-.
BIO 361T: COMPARATIVE ANIMAL PHYSIOLOGY
Physiology of organ systems in animal phyla, with special emphasis on physiological adaptations of organisms to their environment. Three lecture hours and one discussion hour a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Biology 325 or 325H with a grade of at least C-.
BIO 364: MICROBIAL ECOLOGY
The ability of microbes to adapt to and change their environment. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Biology 325 or 325H with a grade of at least C-, and Biology 326R with a grade of at least C-.
BIO 365S: HUMAN SYSTEMS PHYSIOLOGY
Overview of human physiology, including body fluids, the cardiovascular system, respiration, digestion, metabolism, and endocrinology. Three lecture hours and one discussion hour a week for one semester. May not be counted by students with credit for Biology 416L.
- Prerequisite: Biology 311C; Biology 325 or 325H, and Chemistry 301 or 301H with a grade of at least C- in each; and one of the following with a grade of at least C-: Mathematics 408C, 408K, 408N, 408R, or Statistics and Data Sciences 302 (or Statistics and Scientific Computation 302).
BIO 165U: HUMAN SYSTEMS PHYSIOLOGY LABORATORY
Using an inquiry-based approach, provides students with an opportunity for hands-on experience in human physiology. Students read primary scientific literature; collect, analyze, and present data; and write detailed reports on laboratory activities. Four laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- May not be counted by students with credit for Biology 416L.
- Prerequisite: Biology 325 or 325H with a grade of at least C-, and credit or registration for Biology 365S.
BIO 369F: FIELD HERPETOLOGY
Species identification by sight and sound, and research techniques such as sampling populations, data collection, and analysis. One lecture hour and five laboratory hours a week for one semester, with additional field hours to be arranged.
- Prerequisite: The following with a grade of at least C-: Biology 325 or 325H, and Biology 206L, 208L, 226L, or Environmental Science 311.
BIO 369L: HERPETOLOGY
Biology of amphibians and reptiles, including evolution, ecology, behavior, physiology, life history, and identification. Three lecture hours and two laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: The following with a grade of at least C-: Biology 325 or 325H, and Biology 206L, 208L, 226L, or Environmental Science 311.
BIO 370: EVOLUTION
Introduction to modern evolutionary biology, focusing on the evolution of molecular, developmental, morphological, and behavioral traits. Genetic and ecological bases of evolutionary changes within populations and of evolutionary divergence in animals and plants. Three lecture hours and one discussion hour a week for one semester.
- Biology 370 and 385K (Topic 2: Evolution) may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Biology 325 or 325H with a grade of at least C-.
BIO 373: ECOLOGY
An introduction to ecology, the study of relationships among organisms and between organisms and their environment; adaptations, population, communities, and ecosystems. Includes both plants and animals and both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. Three lecture hours and one discussion hour a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Biology 325 or 325H with a grade of at least C-.
BIO 373L: ECOLOGY LABORATORY
Intensive field ecology. Includes group field experiment and observation, independent projects, and field trips to other vegetation zones. Students complete weekly write-ups of observation and data analysis, reports of independent projects, and an oral presentation on an independent project. Four laboratory hours and two workshop/lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Credit with a grade of at least C- or registration for Biology 373; and the following with a grade of at least C-: Biology 206L, 208L, 226L, or Environmental Science 311.
BIO 374: PLANT ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGICAL TECHNIQUES
Tissue organization and cellular details of stems, roots, and leaves of seed plants, with emphasis on development and function. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Biology 325 or 325H with a grade of at least C-, and concurrent enrollment in Biology 174L.
BIO 174L: PLANT ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGICAL TECHNIQUES LABORATORY
Demonstration of cellular details and tissue systems of plant organs; instruction in the preparation of plant materials for histological examination. Three laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Credit with a grade of at least C- or registration for Biology 374; and the following with a grade of at least C-: 206L, 208L, 226L, or Environmental Sciences 311.
BIO 375: CONSERVATION BIOLOGY
Application of principles of ecology to the preservation of wild plant and animal species and to the preservation, management, and restoration of natural and seminatural ecosystems. Emphasis on scientific, biological aspects of issues such as endangered species protection, preserve design, and forest management. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Biology 325 or 325H with a grade of at least C-, and Biology 357, 359J, or 373 with a grade of at least C-.
BIO 446L: HUMAN MICROSCOPIC AND GROSS ANATOMY
Designed for students preparing for biomedical research and the health professions. Focuses on microscopic and gross anatomy of human tissues and organs, with an emphasis on structure function relationships. Subjects include the effects of disease and aging in addition to normal human anatomy. Three lecture hours and four laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: The following courses with a grade of at least C-: Biology 325 or 325H; Chemistry 301; and Mathematics 408C, 408K, 408N, 408R, Statistics and Data Sciences 302 (or Statistics and Scientific Computation 302), or 328M (or Statistics and Scientific Computation 328M).
BIO 448L: INVERTEBRATE BIOLOGY
A study of the diversity and evolution of multicellular invertebrate animals, with emphasis on common themes in animal body construction and function. Three lecture hours and three laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: The following with a grade of at least C-: Biology 325 or 325H, and Biology 206L, 208L, 226L, or Environmental Science 311.
BIO 453L: ENTOMOLOGY
Characteristics, importance, and biology of the major groups of insects. Two lecture hours and three laboratory hours a week for one semester, with additional fieldwork hours to be arranged.
- Prerequisite: The following with a grade of at least C-: Biology 325 or 325H, and Biology 206L, 208L, 226L, or Environmental Science 311.
BIO 455L: VERTEBRATE NATURAL HISTORY
Phylogeny, taxonomy, life histories, habits, and distribution. Two lecture hours and three hours of laboratory or fieldwork a week for one semester, with field trips to be arranged.
- Prerequisite: The following with a grade of at least C-: Biology 325 or 325H, and Biology 206L, 208L, 226L, or Environmental Science 311.
BIO 456L: LIMNOLOGY AND OCEANOGRAPHY
Same as Marine Sciences 440. An introduction to the study of the interactions between aquatic organisms and their environments. Two lecture hours and six laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Chemistry 302 or 302H; and the following with a grade of at least C-: Biology 325 or 325H, and Biology 206L, 208L, 226L, or Environmental Science 311.
BIO 463L: PLANT SYSTEMATICS
Principles of plant classification, phylogeny, and diversity as exemplified by families and species of flowering plants found seasonally in Texas with an emphasis on the local flora. Two lecture hours and three laboratory hours a week for one semester, with additional field trips to be arranged.
- Biology 262 and 262L, and 463L may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: The following with grades of at least C-: Biology 325 or 325H; and Biology 206L, 208L, 226L, or Environmental Science 311.
BIO 471: INTRODUCTION TO SYSTEMATICS
Study of diversification of living and fossil organisms, including speciation, biogeography, taxonomy, and phylogeny of genes, species, and higher taxa. The lecture and laboratory include a significant amount of computational molecular phylogenetics. Three lecture hours and three laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Biology 458L and 471 may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Biology 325 or 325H, and 370 with a grade of at least C-.
BIO 478L: COMPARATIVE VERTEBRATE ANATOMY
Study of vertebrate morphology from developmental anatomy to the function, biomechanics, and phylogenetic relationships of living and fossil taxa. Three lecture hours and four laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Biology 478L and Kinesiology 324K, 424K may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Biology 325 or 325H with a grade of at least C-.
Marine Science Courses
Lower Division Courses
MNS 307: INTRODUCTION TO OCEANOGRAPHY
Introduction to the sciences of oceanography: geological, physical, and biological. Two lecture hours and two laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Marine Sciences 307 and Geological Sciences 307 may not both be counted.
MNS 308: HUMANS AND A CHANGING OCEAN
The consequences of human-induced alteration of the marine environment including the impact on fisheries, marine mammals, food-web changes, and changes in species composition and ecological function will be explored. Designed for non-science majors. Two lecture hours and two laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Marine Sciences 309 (Topic: Humans and a Changing Ocean) and 308 may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Marine Sciences 307 (or Geological Sciences 307).
MNS 310: FUNDAMENTALS OF MARINE SCIENCE
Designed for students pursuing a degree option in Marine and Freshwater Science. In-depth introduction to physical, chemical, geological, and biological processes in marine systems. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Biology 311D and Chemistry 302 or 302H.
Upper Division Courses
MNS 320: MARINE ECOLOGY
Study of ecological processes at different levels of integration in marine ecosystems. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Biology 311D, and Chemistry 302 or 302H.
MNS 120L: LABORATORY STUDIES IN MARINE ECOLOGY
A laboratory course with two weekend field trips to the Marine Science Institute at Port Aransas to perform ecological studies in the Texas coastal zone. Two weekend field trips, with pre- and post-field trip laboratory hours required.
- Prerequisite: Credit or registration for Marine Sciences 320.
MNS 148/348: TRAINING CRUISE(S)
May be repeated for credit when the topics vary.
Topic 1: Training Cruise(s): Research in Biological Oceanography. One or more curistes of one to several days each to collect physical, chemical, oceanographic, and biological data relevant to biological processes in the sea. Prepatory instruction and post-cruise sample processing and analysis.
- Prerequisite: Upper-division standing; consent of instructor; and the following coursework with a grade of at least C- in each: Biology 325 and Chemistry 302 or 302H.
Topic 2: Marine Geology and Geophysics Field Course. Hands on, team-based instruction in the collection and processing of marine geological and geophysical data along the Gulf of Mexico coast. For Marine Science 148, one lecture hour and one laboratory hour a week for one semester. For Geological Sciences 348K and Marine Science 348, one lecture hour and four laboratory hours a week for one semester with additional hours to be arranged. Only one of the following may be counted: Geological Sciences 348K, 397F, Marine Science 348 (Topic 2). Fulfills the field experience requirement for some geological sciences degree programs.
- Students should contact the Department of Geological Sciences before registering.
- Additional prerequisite: For geological sciences majors, Geological Sciences 420K or 320L with a grade of a least C- and consent of instructor; Geological Sciences 416M and 465K are recommended; for others, Marine Science 307 and 354F with a grade of at least C- in each and consent of instructor.
MNS 152L/252L: PRINCIPLES OF MARINE SCIENCE: LABORATORY STUDIES
Lectures, laboratory, and fieldwork. The equivalent of three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- May be repeated for credit when the topics vary.
Topic 9: Endocrinology. Endocrinology, with special reference to lower vertebrates and evolution of control systems.
- Marine Science 352 (Topic 9) and 382 (Topic 9: Endocrinology) may not both be counted. May count as zoology.
- Prerequisite: Previous courses in physiology and consent of instructor.
Topic 12: Adaptive Physiology of Marine Organisms. Selected topics in the comparative physiology of marine organisms and their environmental adaptations.
- Prerequisite: Previous course in cell physiology or consent of instructor.
Topic 13: Microclimatology. Physical and thermal characteristics of the atmospheric surface layer, with particular reference to coastal environments.
Topic 16: Ocean Engineering. Description of ocean waves and tides, methods of wave forecasting, classroom and field exercises.
- Prerequisite: Consent of instructor.
Topic 18: Marine Atmospheric Chemistry. Atmospheric particle chemistry; sea-surface films, atmospheric organic matter; air-sea chemical fractionation; carbon, nitrogen, sulfur cycles.
- Prerequisite: Consent of instructor.
Topic 20: General Marine Phycology. Survey of benthic algae and phytoplankton of the Texas coast; systematics, morphology, life history and culturing techniques.
Topic 21: Ecology of Marine Fungi. Biology of the fungi with emphasis on ecological, morphological, and developmental aspects and culturing techniques.
Topic 22: Oceanography. Consideration of current understanding of the chemistry and biology of the oceans.
MNS 152S/252S: PRINCIPLES OF MARINE SCIENCE: UNDERGRADUATE SEMINAR
Guest lectures by local and visiting research scientists on a variety of topics in marine and environmental science. Each seminar is followed by a separate one-hour discussion to give students an opportunity to meet directly with the scientist. For each semester hour of credit earned, one lecture/discussion a week for one semester.
- May be counted toward the Bachelor of Science in Biology (Option III: Marine and Freshwater Biology) and toward other undergraduate degrees in biology. May be repeated for credit when the topics vary.
MNS 152T/252T: PRINCIPLES OF MARINE SCIENCES: SPECIAL TOPICS
Advanced research topics in marine science relevant to critical habitats, organisms, or processes. The equivalent of one or two lecture hours a week for one semester; additional lecture and field/lab hours may be required.
- May be counted toward the Bachelor of Science in Biology (Option III: Marine and Freshwater Biology) and toward other undergraduate degrees in biology. May be repeated for credit when the topics vary.
- Prerequisite: Upper-division standing and six semester hours of coursework in biology, chemistry, geological sciences, and/or physics.
MNS 170/270/370: SPECIAL STUDIES IN MARINE SCIENCE
Supervised individual instruction and research in marine science field and laboratory techniques. The equivalent of one, two, or three class hours a week for one semester, at the Marine Science Institute at Port Aransas.
- May be repeated for credit.
- Prerequisite: Six semester hours of upper-division coursework in science, a University grade point average of at least 3.00, and written consent of instructor.
MNS 352: PRINCIPLES OF MARINE SCIENCE
Lectures, laboratory, and fieldwork. The equivalent of three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- May be repeated for credit when the topics vary.
Topic 9: Endocrinology. Endocrinology, with special reference to lower vertebrates and evolution of control systems.
- Marine Science 352 (Topic 9) and 382 (Topic 9: Endocrinology) may not both be counted. May count as zoology.
- Prerequisite: Previous courses in physiology and consent of instructor.
Topic 12: Adaptive Physiology of Marine Organisms. Selected topics in the comparative physiology of marine organisms and their environmental adaptations.
- Prerequisite: Previous course in cell physiology or consent of instructor.
Topic 13: Microclimatology. Physical and thermal characteristics of the atmospheric surface layer, with particular reference to coastal environments.
Topic 16: Ocean Engineering. Description of ocean waves and tides, methods of wave forecasting, classroom and field exercises.
- Prerequisite: Consent of instructor.
Topic 18: Marine Atmospheric Chemistry. Atmospheric particle chemistry; sea-surface films, atmospheric organic matter; air-sea chemical fractionation; carbon, nitrogen, sulfur cycles.
- Prerequisite: Consent of instructor.
Topic 20: General Marine Phycology. Survey of benthic algae and phytoplankton of the Texas coast; systematics, morphology, life history and culturing techniques.
Topic 21: Ecology of Marine Fungi. Biology of the fungi with emphasis on ecological, morphological, and developmental aspects and culturing techniques.
Topic 22: Oceanography. Consideration of current understanding of the chemistry and biology of the oceans.
MNS 352C: ESTUARINE ECOLOGY
Explores general ecological principles of estuarine environments in Texas including physiography, hydrography, and plant and animal community structure and productivity. The equivalent of three lecture hours a week for one semester; additional lecture and field/lab hours may be required.
- Marine Sciences 352 (Topic 8) and 352C may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Upper-division standing and six semester hours of coursework in biology, chemistry, geological sciences, or physics.
MNS 352D: MARINE BOTANY
Exploration of the marine algae and seagrasses of the south Texas coast, with emphasis on their taxonomy, physiology, and ecology; may include field trips to representative coastal habitats. The equivalent of three lecture hours a week for one semester; additional lecture and field/laboratory hours may be required.
- Prerequisite: Upper-division standing; one of the following courses: Biology 322, 324, 325 or 325H, 328, Marine Sciences 320, 352C; and three additional semester hours of coursework in biology.
MNS 353: TOPICS IN MARINE SCIENCE
The equivalent of three lecture hours a week for one semester; additional lecture and field/laboratory hours may be required.
- May be repeated for credit when the topics vary.
- Prerequisite: Upper-division standing; consent of instructor.
Topic 2: Fish Adaptations to Coastal Ecosystems. Quantitative ecological comparisons of zoogeographical abundance and distribution with population, metabolic, and growth parameters.
- Additional prerequisite: Fifteen semester hours of coursework in biology and/or zoology.
Topic 4: Current Research. Research instruction/participation in marine science. Laboratory and field activity with emphasis on faculty contact.
Topic 5: Seafloor Mining. Study of seafloor mineral resources, including problems and policies related to exploration, mining, environmental concerns, assessment, and industrial development.
Topic 6: Marine Ecology. Independent study in marine ecology, literature research, and comprehensive writing. Report required.
- Additional prerequisite: Upper-division standing in a natural science, engineering, or education.
Topic 7: Marine Sedimentology. Selected topics and problems concerning the depositional processes, controls, and distribution of marine sediments.
Topic 8: Marine Chemistry. Study of the processes controlling the chemistry of natural waters, the oceans as a chemical system, and the impact of human activities on these systems.
Topic 14: Marine Isotope Geochemistry. The use of isotopes (stable, radiogenic, uranium series, and anthropogenic) in the study of marine science.
Topic 15: Interdisciplinary Classroom Field Methods. Uses the interdisciplinary nature of marine science to focus on inquiry-based instruction, constructivist-oriented teaching strategies, and field explorations.
Topic 17: Marine Fish Physiology. Physiology of major organ systems of marine fishes, with emphasis on adaptations to marine environments. Includes osmoregulation, nutrition, circulation, excretion, reproduction, sensory physiology, and endocrine control.
- Additional prerequisite: Biology 311D, and Chemistry 302 or 302H.
MNS 354: MARINE INVERTEBRATES
Study of invertebrate taxonomy, structure, behavior, and ecology; may include field sampling and laboratory studies of invertebrate habitats of the Texas coast. The equivalent of three lecture hours a week for one semester; additional lecture and field/laboratory hours may be required.
- Prerequisite: Upper-division standing; six semester hours of biology coursework.
MNS 354C: BIOLOGY OF FISHES
Anatomy, physiology, behavior, life history, taxonomy, and distribution of fishes; may include field sampling and laboratory studies of the coastal biota. The equivalent of three lecture hours a week for one semester; additional lecture and field/laboratory hours may be required.
- Prerequisite: Upper-division standing, six semester hours of coursework in biological sciences, or consent of instructor.
MNS 354E: AQUATIC MICROBIOLOGY
Ecology, physiology, distribution, and growth of heterotrophic and autotrophic bacteria and fungi in waters and sediments. The equivalent of three lecture hours a week for one semester; additional lecture and field/laboratory hours may be required.
- Marine Sciences 354E and 384E may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Biology 311D, Chemistry 302 or 302H; and consent of instructor.
MNS 354Q: MARINE ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE
Application of the principles of marine science to the study of environmental issues: toxicology, biogeochemical cycles, and the biological and ecological impacts of zenobiotic materials in the coastal zone. The equivalent of two lecture hours and one laboratory hour a week for one semester; additional lecture and field/laboratory hours may be required.
- Prerequisite: Upper-division standing; Biology 311D, and Chemistry 302 or 302H.
MNS 354T: BIOLOGICAL OCEANOGRAPHY
Introduction to the organisms in the sea, their adaptations to the environment, and the factors that control their distribution and abundance; may include laboratory and field work with organisms found in the coastal waters of Texas. The equivalent of three lecture hours a week for one semester; additional lecture and field/laboratory hours may be required.
- Prerequisite: Upper-division standing and Biology 311D.
MNS 354U: BIOLOGY OF SHARKES, SKATES, & RAYS
Ecology, anatomy, and physiology of elasmobranch fishes. The equivalent of three lecture hours a week for one semester; additional lecture and field/laboratory hours may be required.
- Prerequisite: Upper-division standing, Biology 311D, and Chemistry 302 or 302H.
MNS 355C: PHYSIOLOGY OF FISHES
Physiology of major organ systems of both marine and freshwater fishes. The equivalent of three lecture hours a week for one semester; additional lecture and field/laboratory hours may be required.
- Prerequisite: Upper-division standing, Biology 311D, and Chemistry 302 or 302H.
MNS 356: ECOSYSTEM OCEANOGRAPHY
An exploration of interconnections within and among marine ecosystems, as well as their linkages to climate, human activity, and adjacent freshwater and terrestrial environments. Emphasis will be placed on Gulf of Mexico ecosystems; may include hands-on field and laboratory activities. The equivalent of three lecture hours a week for one semester; additional lecture and field/laboratory hours may be required.
- Marine Sciences 352 (Topic: Ecosystem Oceanography) and 356 may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Upper-division standing; Biology 311D; and Chemistry 302 or 302H.
MNS 357: MARINE PHYTOPLANKTON DIVERSITY
The taxonomy of the major phytoplankton groups, their physiology, and their role in marine ecosystem; may include field and/or laboratory hours. The equivalent of three lecture hours a week for one semester; additional lecture and field/laboratory hours may be required.
- Marine Sciences 353 (Topic: Diversity Marine Phytoplankton) and 357 may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Upper-division standing; Biology 311D; and Chemistry 302 or 302H.
MNS 367K: HUMAN EXPLORATION AND EXPLOITATION OF THE SEA
Review of the history of ocean exploration including major oceanographic expeditions. Discussion of current topics in ocean exploration and exploitation of marine resources, the impact of resource exploitation on biological systems, and the development of marine policy. An oral presentation is required. The equivalent of three lecture hours a week for one semester; additional lecture and field/laboratory hours may be required.
- Prerequisite: Bio 311H or BIO 315H and Chem 302 or 302H
MNS 440: LIMNOLOGY AND OCEANOGRAPHY
Same as Biology 456L. An introduction to the study of the interactions between aquatic organisms and their environments. Two lecture hours and six laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Chemistry 302 or 302H; and the following with a grade of at least C-: Biology 325 or 325H, and Biology 206L, 208L, 226L, or Environmental Science 311.
Molecular Biosciences Courses
MBS Course Descriptions
Lower Division Courses
BCH 206K: UNDERGRADUATE RESEARCH
Introduction to research practices; supervised individual undergraduate research in biochemistry. Six to ten laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- May be taken for a letter grade no more than twice. No more than six semester hours may be counted toward a degree in biochemistry. May be repeated for credit.
Upper Division Courses
BCH 339F: FOUNDATIONS OF BIOCHEMISTRY
Restricted to biochemistry majors. Metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids, amino acids, and nucleotides; structure and function of proteins. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Only one of the following may be counted: Biochemistry 339F, 369, Biology 337 (Topic: Foundations of Biochemistry), Chemistry 339K, 369.
- Prerequisite: One of the following with a grade of at least C-: Chemistry 310M, 318M, 320M, or 328M.
BCH 339JL CHEMICAL & SYNTHETIC BIOLOGY
Designed for students pursuing pharmaceutical and biotechnology careers. Topics include enzymatic reaction mechanisms and how they can be manipulated using tools from both chemistry and molecular biology. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Only one of the following may be counted: Biochemistry 339J, Chemistry 339J, Systems and Synthetic Biology 339J.
- Prerequisite: Biochemistry 339F or Chemistry 339K with a grade of at least C-.
BCH 339M: STRUCTURE & FUNCTION OF MOLECULAR MACHINES
Function of proteins and protein complexes as machines in the cell, including the interaction of proteins with nucleic acids, synthesis of proteins, and degradation of proteins. Three lecture hours per week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Biochemistry 339F or Chemistry 339K with a grade of at least C-.
BCH 339N: SYSTEMS BIOLOGY & BIOINFORMATICS
Restricted to biochemistry majors. Understanding how the cell works as a system with emphasis on the methods used to gather and analyze data and develop/test models of systems level data. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Only one of the following may be counted: Biochemistry 339N, 350, Biology 337 (Topic: Quantitative Analysis of Cellular and Molecular Biology), Chemical Engineering 337, 379 (Topic: Quantitative Analysis of Cellular and Molecular Biology), 381Q.
- Prerequisite: Biochemistry 339F or Chemistry 339K with a grade of at least C-.
BCH 364C: BIOINFORMATICS
*MEETS WITH GRADUATE COURSE WHEN OFFERED
Restricted to biochemistry majors. Subjects include physical methods for the study of macromolecules, chemistry of proteins, enzyme chemistry, regulatory mechanisms for gene expression, and protein-nucleic acid interactions. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Only one of the following may be counted: Biochemistry 364C, Chemistry 364C, Systems and Synthetic Biology 364C.
- Prerequisite: Biochemistry 339F or Chemistry 339K with a grade of at least B, and consent of instructor.
BCH 364E: SYSTEMS BIOLOGY
*MEETS WITH GRADUATE COURSE WHEN OFFERED
Restricted to biochemistry majors. Survey of current high-throughput technologies and computational methods for generating data and integrating information at all levels of biological organization. Emphasis on how hypotheses can be generated and tested with these techniques to better understand how model organisms function and evolve. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Biochemistry 364E and Chemistry 364E may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Biochemistry 339 or Chemistry 339K with a grade of at least B, and consent of instructor.
BCH 364F: BIOCHEMISTRY OF ASTROBIOLOGY
Restricted to biochemistry majors. An overview of the science used in the search for extraterrestrial life, life origins, earth history, evolution, metabolism of extremophiles, biochemistry, and astronomy. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Biochemistry 364F and Chemistry 364F may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Biochemistry 339F or Chemistry 339K with a grade of at least B, or consent of instructor.
BCH 365D: STRUCTURE & FUNCTION OF PROTEINS & NUCLEIC ACIDS
*MEETS WITH GRADUATE COURSE WHEN OFFERED
Restricted to biochemistry majors. Exploration of the structures and functions of proteins and nucleic acids, utilizing quantitative methods to evaluate the roles of structural features in function, and developing new ways of thinking about the dynamics of macromolecules. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Biochemistry 365D and Chemistry 365D may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: The following with a grade of at least B: Biochemistry 339F or Chemistry 339K, Biochemistry 370 or Chemistry 370, and consent of instructor.
BCH 369: FUNDAMENTAL OF BIOCHEMISTRY (NON-MAJORS)
The basics of protein structure and function, carbon and nitrogen metabolism, and molecular biology of macromolecules. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Only one of the following may be counted: Biochemistry 339F, 369, Biology 337 (Topic: Foundations of Biochemistry), Chemistry 339K, 369. May not be counted toward a degree in biochemistry.
- Prerequisite: One of the following with a grade of at least C-: Chemistry 310M, 318M, 320M, or 328M.
BCH 369K: TECHNIQUES OF RESEARCH (INDEPENDENT RESEARCH)
Advanced laboratory practice and introduction to research. One lecture hour and six laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- May be taken for a letter grade no more than twice. No more than six semester hours may be counted toward a degree in biochemistry. May be repeated for credit.
- Prerequisite: Six semester hours of upper-division coursework in biochemistry or chemistry, or five semester hours of coursework in organic chemistry, or consent of the undergraduate faculty adviser in biochemistry.
BCH 369L: BIOCHEMISTRY LABORATORY
An introduction to modern fundamental techniques of biochemistry. Two lecture hours and seven laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Biochemistry 369L and Chemistry 369L may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Biochemistry 339F or Chemistry 339K with a grade of at least C-.
BCH 369T: BIOTECHNOLOGY LABORATORY
Advanced techniques in biotechnology. Nine laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Biochemistry 369T and Chemistry 369T may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Consent of instructor.
BCH 370: PHYSICAL METHODS FOR BIOCHEMISTRY
Theory of electrophoresis, ultracentrifugation, spectroscopy, electron microscopy, and diffraction as applied to biological macromolecules. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Biochemistry 370 and Chemistry 370 may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Biochemistry 339F or Chemistry 339K with a grade of at least C-.
BIO 160L: IMMUNOLOGY LABORATORY
Current techniques in experimental cellular and humoral immunology. Three laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: The following with a grade of at least C-: Biology 325 or 325H, and 206L, 208L, 226L, or Environmental Science 311.
BIO 226L: GENERAL MICROBIOLOGY LABORATORY
Introduction to microbiology laboratory techniques and experimental demonstration of principles of microbiology. One lecture and three laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Credit with a grade of at least C- or registration for Biology 326M or 326R.
BIO 230L: VIROLOGY LABORATORY
Basic experimental techniques applied to selected bacteriophages and animal viruses. Four laboratory hours and one discussion hour a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Biology 226L with a grade of at least C-, and credit with a grade of at least C- or registration for Biology 330.
BIO 320: CELL BIOLOGY
Principles of eukaryotic cell structure and function; macromolecules, membranes, organelles, cytoskeleton, signaling, cell division, differentiation, motility, and experimental methodologies. Three lecture hours and one discussion hour a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Biology 325 or 325H with a grade of at least C-.
BIO 320L: CELL BIOLOGY LABORATORY
Explores the complex structures and functions of cells through direct observation and experimentation. Subjects may include regulation of gene transcription and translation, protein sorting, organelles and membrane trafficking, cytoskeletal dynamics, and cell division. Students use a combination of modern molecular biology, biochemistry, and microscopy techniques, with a strong emphasis placed on hypothesis-driven approaches, proper experimental design, and clear scientific writing and presentation. One lecture hour and five laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: The following with a grade of at least C-: Biology 325 or 325H, and Biology 206L, 208L, 226L, or Environmental Sciences 311; and credit with a grade of at least C- or registration for Biology 320.
BIO 323L: LABORATORY STUDIES IN CELL BIOLOGY
Research exercises involving light/electron microscopy, image processing, autoradiography, chromatography, fractionation, flow cytometry, spectroscopy, diffraction, antibody labeling, cell growth, and kinetics. One lecture hour and four laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: The following with a grade of at least C-: Biology 325 or 325H, and Biology 206L, 208L, 226L, or Environmental Sciences 311; and credit or registration for Biology 320.
BIO 326M: INTRODUCTORY MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY & IMMUNOLOGY
Designed primarily for nursing and prepharmacy students. Overview of the structure, function, and genetics of bacteria, viruses, and fungi, with emphasis on the interactions between micro-organisms and the human host. Includes principles of microbial pathogenesis, the host's innate and adaptive immune responses to infection, epidemiology, laboratory diagnosis, and antimicrobial chemotherapy and vaccines. Three lecture hours and one discussion hour a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Biology 311C; Biology 325 or 325H with a grade of at least C-; Chemistry 301 with a grade of at least C-; and one of the following with a grade of at least C-: Mathematics 408C, 408K, 408N, 408R, Statistics and Scientific Computation 302.
BIO 326R: GENERAL MICROBIOLOGY
Overview of the major areas of microbiological study, including cell structure and function, genetics, host-microbe interactions, physiology, ecology, diversity, and virology. Three lecture hours and one discussion hour a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Credit with a grade of at least C- or registration for Biology 325 or 325H, and Chemistry 302 or 302H with a grade of at least C-.
BIO 372E: EPIGENETICS
A study of epigenetic modifications, the covalent modifications of DNA or histones that cause changes in gene expression. Particular attention is given to how experience or environmental factors epigenetically modify health or behavior in animals. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Biology 327E and 337 (Topic: Epigenetics) may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Biology 325 or 325H with a grade of at least C-.
BIO 327G: GENOMICS
Genome structure, organization, and function of model organisms; theory and methodology of genetic and physical mapping; sequencing analysis and annotation; genome duplication and evolution; and ethics for biotechnology and cloning. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Biology 327G and 337 (Topic: Genomics) may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Biology 325 or 325H with a grade of at least C-.
BIO 328: INTRODUCTORY PLANT PHYSIOLOGY
General principles of the mineral nutrition, water relations, metabolic activities, growth and development of green plants. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Biology 325 or 325H with a grade of at least C-, and Chemistry 302 or 302H.
BIO 330: MOLECULAR BIOLOGY OF ANIMAL VIRUSES
Mechanisms by which viruses replicate and kill or transform cells. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Biology 325 or 325H, and 326M or 326R with a grade of at least C- in each.
BIO 331L: LABORATORY STUDIES IN MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
The methods and principles of molecular biology in a research laboratory context. Students conduct a research project directed by a faculty member. One lecture hour and four and one-half laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: The following with a grade of at least C-: Biology 325 or 325H, and Biology 206L, 208L, 226L, or Environmental Sciences 311.
BIO 335: INTRODUCTION TO BIOCHEMICAL ENGINEERING
Microorganisms in chemical and biochemical synthesis; genetic manipulation of cells by classical and recombinant DNA techniques. Enzyme technology; design of bioreactors and microbial fermentations; separations of biological products. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Only one of the following may be counted: Biology 335, Biomedical Engineering 339, Chemical Engineering 339, 379 (Topic: Introduction to Biochemical Engineering).
- Prerequisite: Biochemistry 339F (or Chemistry 339K) or 369 (or Chemistry 369), and Biology 311C with a grade of at least C-.
BIO 336: TUMOR BIOLOGY
Covers core aspects of cancer pathology, treatment, epidemiology, the discovery of oncogenes and tumor suppressors, and the molecular genetics underlying the characteristic features of malignant tumors (including metastatic behavior, genomic instability, angiogenesis, cell cycle regulation, and apoptosis). Strong emphasis on the biochemical functions of cancer-related proteins and enzymes and therapeutic approaches based on our understanding of these proteins. Important experimental approaches that have influenced our current understanding of cancer will also be stressed. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Biology 336 and 391M may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Biology 325 or 325H with a grade of at least C-, and Biology 330 or 360K with a grade of at least C-.
BIO 339: METABOLISM AND BIOCHEMISTRY OF MICROORGANISMS
A study of the metabolic processes of microorganisms, using a biochemical approach. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Biology 339 and 391R may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Biology 326R with a grade of at least C-.
BIO 344: MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
Molecular basis of cellular processes: gene structure and function, DNA replication, RNA and protein synthesis, viruses, molecular aspects of immunology and cancer, and recombinant DNA. Three lecture hours and one discussion hour a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Biology 325 or 325H with a grade of at least C-.
BIO 349: DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY
Principles of animal development, with emphasis on developmental mechanisms. Three lecture hours and one discussion hour a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Biology 325 or 325H with a grade of at least C-.
BIO 349L: EXPERIMENTS IN DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY
An investigation of methods and principles of developmental biology in a laboratory context, with emphasis on animal embryology using molecular techniques and microscopy. One lecture hour and six laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: The following with a grade of at least C-: Biology 325 or 325H, and Biology 206L, 208L, 226L, or Environmental Science 311; and credit with a grade of at least C- or registration for Biology 349.
BIO 350M: PLANT MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
Fundamentals of plant molecular biology, including structure and expression of the chloroplast and mitochondrial genomes. Three lecture hours a week for one semester. Biology 350M and 388M may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Biology 325 or 325H with a grade of at least C-.
BIO 354C: CELL BIOLOGY OF HUMAN BIRTH DEFECTS
Explores the link between basic cell biology, human genetics, and human birth defects using current scientific literature exposing students to critical thinking and the scientific method, as well as the application of these tools to the study of biology. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Biology 337 (Topic: Developing Biology) and Biology 354C may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Biology 349 with a grade of at least C-.
BIO 360K: IMMUNOLOGY
The basic concepts of humoral and cell-associated immune phenomena. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: The following with a grade of at least C-: Biology 325 or 325H, and Biology 326R or 326M.
BIO 360M: MOLECULAR IMMUNOLOGY
An advanced immunology course with an emphasis on molecular models and medical relevance. Three lecture hours a week for one semester. Biology 337 (Topic: Molecular Immunology) and 360M may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Biology 325 or 325H with a grade of at least C-, and Biology 360K with a grade of at least B-.
BIO 361: HUMAN INFECTIOUS DISEASES
Etiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and immunobiology of the major microbial diseases, with emphasis on their prevention. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Biology 325 or 325H, and Biology 326M or 326R with a grade of at least C- in each.
BIO 361L: CLINICAL BACTERIOLOGY LAB
Training in techniques required for independent work in diagnostic and epidemiological bacteriology. Two lecture hours and five laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: The following with a grade of at least C- in each: Biology 325 or 325H; 226L; and 326R or 326M.
BIO 366: MICROBIAL GENETICS
Molecular biology of nucleic acids; biosynthesis of macromolecules, transfer of genetic material from cell to cell, recombination, mutagenesis, and regulatory mechanisms. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Biology 366 and 391S may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Biology 325 or 325H with a grade of at least C-, and Biology 326R with a grade of at least C-.
BIO 366R: MOLECULAR GENETICS IN MEDICINE
Implementation of molecular genetics techniques in medicine. Includes application of diagnostic and therapeutic techniques for several genetic disorders and infectious diseases. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Biology 325 or 325H with a grade of at least C-.
Neuroscience Courses
Upper Division Courses
BIO 367C: CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR BASIS OF NEURAL DEVELOPMENT
An introduction to the principles by which the neural tube (brain and spinal cord) forms during embryonic development. Subjects include the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying the formation of a three-dimensional neural tube and its division into forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain, and spinal cord. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Biology 365N and Biology 367C may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: One of the following with a grade of at least C-: Biology 325, Neuroscience 330, 365R.
BIO 371L: EXPERIMENTAL PHYSIOLOGY
Experimental approach to physiological mechanisms by which animals adapt to their environment. One lecture hour, four laboratory hours, and two hours of computer work a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: The following with a grade of at least C-: Biology 325 or 325H, and Biology 206L, 208L, 226L, or Environmental Science 311.
NEU 330: NEURAL SYSTEMS I
Introduction to the nervous system with an emphasis on brain organization, neuron physiology, perceptual systems, and motor systems. Intended for neuroscience majors and those considering neuroscience as a major. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Only one of the following may be counted: Biology 337 (Topic: Neural Systems I), 365R, 371M, Neuroscience 330, 365R, 371M.
NEU 335: NEURAL SYSTEMS II
Introduction to the nervous system with an emphasis on neural development and on the neural mechanisms of memory, emotions, and other higher cognitive functions. Intended for neuroscience majors and those considering neuroscience as a major. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Only one of the following may be counted: Biology 335, 337 (Topic: Neural Systems II), Neuroscience 335.
- Prerequisite: The following with a grade of at least C-: Biology 206L, and 311D or 325H; Mathematics 408C or 408S; Neuroscience 330; and Physics 303L, 316, or 317L.
NEU 365D: PRINCIPLES OF DRUG ACTION
Introduction to the basic principles of pharmacology; including how drugs get into the body, exert their actions, and are metabolized and excreted. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Biology 365D (Topic: Principles of Drug Action) and Neuroscience 365D may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Neuroscience 335 with a grade of at least C-.
NEU 365L: NEUROBIOLOGY LABORATORY
An introduction to physiological, morphological, and molecular techniques used for analysis of the nervous system. Experiments and computer simulations illustrate basics of information processing by the nervous system. Four laboratory hours and one discussion hour a week for one semester.
- Biology 365L (Topic: Neurobiology Laboratory) and Neuroscience 365L may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Neuroscience 335 with a grade of at least C-.
NEU 365T: NEUROBIOLOGY OF DISEASE
The neurobiological basis of disorders of the brain, with the main focus on mental illness. Emphasizes the neural circuitries and neurochemical events that underlie specific mental processes and behaviors. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Biology 365T and Neuroscience 365T may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Neuroscience 335 with a grade of at least C-.
NEU 365W: NEUROBIOLOGY OF ADDICTION
Study of the neurobiology of neurotransmitters, and the influence of alcohol and drugs of abuse on neurotransmitters. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Biology 365W and Neuroscience 365W may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Neuroscience 335 with a grade of at least C-.
NEU 366C: ION CHANNELS & THE MOLECULAR PHYSICS OF NEURONAL SIGNALING
Explores the role of molecular conformational changes in higher-level neuronal function and sensory transduction, including the generation and regulation of diverse types of neuronal signaling characteristics. Emphasizes a quantitative approach and the use of models to study function. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Only one of the following may be counted: Biology 337 (Topic: Ion Channels and the Molecular Physiology of Neuronal Signaling), 366C, Neuroscience 366C.
- Prerequisite: Neuroscience 335 with a grade of at least C-.
NEU 366D: SYNAPTIC PHYSIOLOGY & PLASTICITY
Detailed study of the physiology of synaptic transmission in the mammalian central nervous system. Covers dendritic integration and various forms and mechanisms of synaptic plasticity. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Only one of the following may be counted: Biology 337 (Topic: Synaptic Physiology and Plasticity in the Central Nervous System), 366D, Neuroscience 366D.
- Prerequisite: Neuroscience 335 with a grade of at least C-.
NEU 366E: VISUAL NEUROSCIENCE
Physiology of the visual pathway and its relationship to visual perception; prospects for prevention of blinding eye diseases; functional and ecological adaptations of primate vision. Laboratory experiments and demonstrations illustrate and extend lecture topics and include measurement of several aspects of students' own visual and sensorimotor function. One and one-half lecture hours and three laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Only one of the following may be counted: Biology 337 (Topic: Visual Neuroscience), 366E, 366P, Neuroscience 366E, 366P.
- Prerequisite: Biomedical Engineering 365R or Neuroscience 335 with a grade of at least C-.
NEU 366L: NEUROIMAGING LABORATORY
Basic principles of image formation and techniques of fluorescent imaging and confocal laser-scanning microscopy. Includes image processing and analysis to extract quantitative information from digital images. Survey of imaging techniques, including electron microscopy and functional MRI. One lecture hour and four laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Only one of the following may be counted: Biology 337 (Topic: Microscopy and Fluorescence Imaging Laboratory), 366L, Neuroscience 366L.
- Prerequisite: Neuroscience 335 with a grade of at least C-.
NEU 466M: QUANTITATIVE METHODS IN NEUROSCIENCE I
Overview of the basic mathematical and computational tools central to the analysis of neural systems in a laboratory setting. Subjects include linear algebra, differential equations, filtering, correlation, probability, and inference, with an emphasis on quantitative methodology and applications to neuroscience. Three lecture hours and one and one-half laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Prerequisite: Mathematics 408D or 408M, and Neuroscience 335 with a grade of at least C- in each.
NEU 366N: QUANTITATIVE METHODS IN NEUROSCIENCE II
Continuation of Neuroscience 466M. Introduction to basic mathematical and computational tools for the analysis of neural systems. Subjects include computational and quantitative methods, with an emphasis on their applications to neuroscience. Three lecture hours and one laboratory hour a week for one semester.
- Biology 366N and Neuroscience 366N may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Neuroscience 466M with a grade of at least C-.
NEU 366P: LABORATORY IN PSYCHOPHYSICS
Studies the principles of experimental design, execution, and interpretation by having students measure their own perceptual and behavioral responses to visual and auditory tests. Includes data analysis, statistical significance, and interpretation. Five laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Only one of the following may be counted: Biology 337 (Topic: Visual Neuroscience), 366E, 366P, Neuroscience 366E, 366P.
- Prerequisite: Neuroscience 335 with a grade of at least C-.
NEU 366S: NEOROMOLECULAR GENETICS & DISEASE LAB
Explores techniques used to study the molecular genetic basis for nervous system function and disease with a powerful invertebrate model system. Subjects will range from studying the conserved molecular basis for our senses and male/female-specific behaviors, to exploring how mutations of conserved neural genes cause neurological disorders, such as Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease. Six laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Biology 366S and Neuroscience 366S may not both be counted.
- Prerequisite: Neuroscience 335 with a grade of at least C-.
NEU 367F: FOUNDATIONS OF HUMAN NEUROIMAGING
Survey of methods for neuroimaging research. Describes the physics of MRI image acquisition, the physiology of neural responses, and the design and analysis of MRI studies. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Only one of the following may be counted: Biology 337 (Topic: Foundations of Human Neuroimaging), 367F, Neuroscience 367F.
- Prerequisite: Neuroscience 330 or 365R (or Biology 365R) with a grade of at least C-.
NEU 367V: EVOLUTIONARY NEUROBIOLOGY
Examination of the nervous system in an evolutionary context. Three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- Only one of the following may be counted: Biology 337 (Topic: Evolutionary Neurobiology), 367V, Neuroscience 367V.
- Prerequisite: Biology 325 or 325H with a grade of at least C-.
NEU 379H: HONORS TUTORIAL COURSE
Restricted to students in the honors program in neuroscience. Original laboratory research project under the direction of a faculty mentor leading to a thesis or research presentation. The equivalent of one, two, or three lecture hours a week for one semester.
- May be repeated for credit, but no more than six hours may be counted toward a degree in neuroscience.
- Prerequisite: Consent of student's research supervisor and the departmental honors adviser.
NEU 466G: FUNCTIONAL & SYNAPTIC NEUROANATOMY
Neuroanatomy and functional connectivity as a basis for brain function and behavior examined from gross structure, cytology, and nanoscale synaptic connectivity in the somatosensory, motor, visual, auditory, olfactory, taste, limbic, vestibular, hypothalamus, and other symptoms. Examination of the synaptic basis of learning and memory, fear, sleep, stress, and synaptic changes during development, aging, mental retardation, and neurological diseases. Laboratory projects involve three-dimensional reconstructions from serial section electron microscopy. Three lecture hours and one and one half laboratory hours a week for one semester.
- Only one of the following may be counted: Biology 337 (Topic: Neurobiology of Synaptic Circuits), 337 (Topic: Human Neuroanatomy), 366F, Neuroscience 466G.
- Prerequisite: Neuroscience 335with a grade of at least C-.
For questions regarding courses and registration, please send us an email!